What Is a Modular House and How Does It Work?
2026-02-05 02:15:26
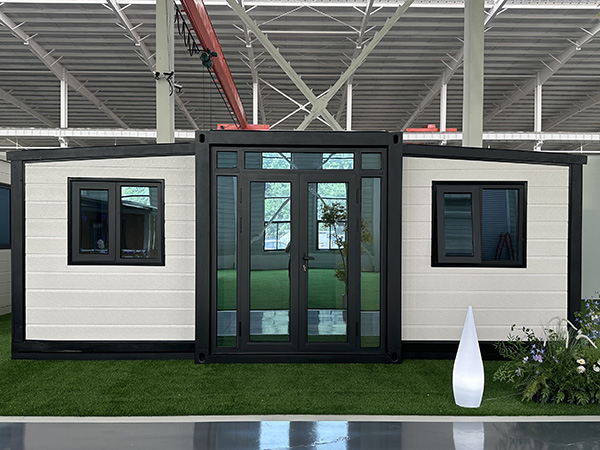

A modular house is a prefabricated building constructed from factory-manufactured, standardized "modules" (self-contained functional units like bedrooms, bathrooms, or living rooms) that are transported to the site and assembled into a complete structure. Unlike traditional on-site construction, its core advantage lies in off-site precision production + on-site rapid assembly, combining efficiency, quality control, and flexibility.
What Is a Modular House?
Core Definition: Modules are prefabricated in a factory (including structural frames, walls, floors, ceilings, internal and external finishes, and even built-in furniture/appliances) according to unified design standards. After production, they are transported by trucks to the construction site, then hoisted and spliced into a whole building via bolts, connectors, or precast joints.
Key Features:
Standardization: Modules follow industry size standards (e.g., 20ft/40ft container-derived sizes or custom standardized dimensions) to ensure compatibility during assembly and transportation.
Factory Production: Constructed in a controlled environment, avoiding weather-related delays and ensuring consistent quality (e.g., precise welding, uniform insulation installation).
Rapid Assembly: On-site assembly typically takes days to weeks (vs. months for traditional construction), significantly shortening the project timeline.
Flexibility: Modules can be combined, expanded, or relocated—e.g., adding a bedroom module to a single-story house, or moving the entire structure to a new site.
How Does a Modular House Work? (Full Process Breakdown)
The workflow spans design, factory production, transportation, on-site assembly, and final commissioning, with strict coordination between each link:
1. Design & Planning (Lay the Foundation)
Collaborate with architects and engineers to finalize functional needs (residential/office/temporary use), floor plans, and module splitting logic (e.g., splitting a house into "bedroom modules," "kitchen-bath modules," etc.).
Ensure module sizes comply with transportation limits (usually width ≤ 3.5m, length ≤ 12m) and local building codes (seismic, wind resistance, energy efficiency standards).
Standardize interfaces: Unify structural connection points, water/electricity pipeline ports, and waterproof details to ensure seamless splicing.
2. Factory Prefabrication (Precision Production)
Structural Manufacturing: Fabricate steel, wood, or concrete frames (steel is the most common) and install walls, floors, and ceilings with insulation and waterproof layers.
Interior & Exterior Finishing: Complete internal painting, flooring, door/window installation, and external cladding (e.g., metal panels, wood) in the factory.
M&E Integration: Pre-install plumbing, electrical wiring, HVAC systems, and even appliances (refrigerators, air conditioners) with reserved connection interfaces.
Quality Inspection: Conduct strict tests (waterproof, structural load-bearing, electrical safety) before modules leave the factory to ensure compliance with standards.
3. Transportation to Site
Use flatbed trucks to transport modules (stacked compactly to reduce trips and carbon emissions).
Secure modules with fixtures during transportation to prevent deformation or damage to finishes/pipelines.
Coordinate with transportation routes to avoid height/width restrictions (e.g., bridges, tunnels).
4. On-Site Assembly (Rapid Splicing)
Foundation Preparation: Build a simple, stable foundation (strip foundation, concrete piers) in advance—faster and less labor-intensive than traditional foundations.
Module Hoisting: Use cranes to lift modules onto the foundation and position them according to design drawings (e.g., aligning bedroom modules with living room modules).
Structural Connection: Secure modules with high-strength bolts or connectors to form a rigid whole; seal splicing seams with waterproof sealants and metal strips to prevent water leakage/air infiltration.
M&E Connection: Connect pre-reserved water, electricity, and HVAC pipelines between modules to ensure system integration.
5. Finishing & Commissioning
Complete on-site touch-ups: Fill gaps between modules, install exterior trim, and finish landscaping.
Conduct comprehensive inspections: Test water/electricity systems, structural stability, and energy efficiency (e.g., thermal insulation performance).
Obtain occupancy permits after passing local authorities’ acceptance.
References
GB/T 7714:Zohourian M, Pamidimukkala A, Kermanshachi S, et al. Modular Construction: A Comprehensive Review[J]. Buildings, 2025, 15(12): 2020.
MLA:Zohourian, Mohammadamin, et al. "Modular Construction: A Comprehensive Review." Buildings 15.12 (2025): 2020.
APA:Zohourian, M., Pamidimukkala, A., Kermanshachi, S., & Almaskati, D. (2025). Modular Construction: A Comprehensive Review. Buildings, 15(12), 2020.