How to ensure the sustainability of modular houses?
2026-02-05 02:03:00
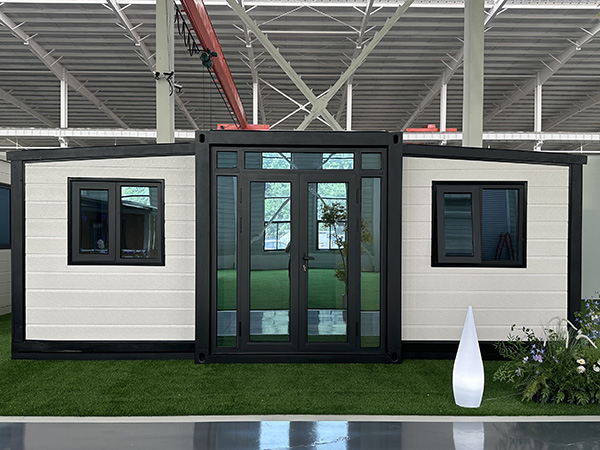

How to ensure the sustainability of modular houses?
To ensure the sustainability of modular houses, the core focuses on three dimensions: environmental protection cycle of materials, efficient use of energy, and adaptive iteration of design, combining the advantages of factory production and life cycle management, which can be achieved through the following key measures:
1. Give priority to green, low-carbon and recyclable materials.
Structural materials: choose renewable/low-carbon building materials, such as cross laminated wood (CLT), laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and other engineering wood (with lower hidden carbon than steel and concrete), or recycled steel and recycled plastic components.
Enclosure materials: adopt environmental protection insulation layer (such as rock wool and glass wool, avoiding EPS board containing formaldehyde) and recyclable metal roof/wall to reduce the use of non-degradable materials.
Auxiliary materials: low VOC (volatile organic compounds) paint and aldehyde-free adhesive are selected to reduce indoor pollution, and the materials need to be marked with recyclable labels to facilitate later disassembly and classification.
2. Optimize the energy system and reduce the whole cycle energy consumption.
Passive energy-saving design: high-efficiency insulation layer, double-layer Low-E glass and doors and windows with excellent sealing performance are integrated during factory prefabrication to reduce cold and heat exchange; Rationally plan the building orientation, maximize the use of natural lighting and ventilation, and reduce the energy consumption of air conditioning and lighting.
Active clean energy configuration: reserve the installation interface of solar photovoltaic panels and the installation position of wind energy equipment, or directly integrate the solar hot water system to meet some domestic electricity/water demand and reduce the dependence on fossil energy.
Intelligent energy consumption management: embedded with intelligent electricity meter and temperature control system, real-time monitoring of water and electricity usage, and optimization of energy distribution (such as electricity storage at night low electricity price and automatic adjustment of indoor temperature and humidity).
3. The modular design of "disassembly and reuse" is adopted.
Modular split logic: ensure that the interfaces of functional modules (such as bedroom and bathroom modules) are standardized and the connection mode is detachable (avoiding welding and fixing), and can be replaced, upgraded or moved to other projects for reuse in the later stage.
Reserved expansion space: The expansion interface is reserved for the module structure, which can flexibly add modules or adjust the internal layout to prolong the service life of the building according to the changes of family population and use scenarios (such as changing from single apartment to family residence).
Easy-to-maintain design: key components (such as pipelines and circuits) are centrally arranged and easy to repair, reducing material waste and structural damage during maintenance.
4. Factory production+green construction to reduce environmental impact.
Advantages of factory prefabrication: accurate production in controlled environment, material utilization rate can reach more than 90% (much higher than 70% of traditional on-site construction), reducing waste generation; Concentrate on dust and noise in the production process to reduce the pollution to the surrounding environment.
Low-carbon construction process: module transportation adopts compact stacking mode to reduce transportation trips and carbon emissions; The site only needs hoisting and splicing, without large-scale excavation and on-site pouring, which shortens the construction period and reduces the energy consumption in the construction stage.
5. Life cycle management, closed-loop recycling.
Pre-planning: In the design stage, evaluate the recyclability of materials and the disassembly of modules, and work out the later recycling scheme (such as steel recycling and wood reprocessing).
Operation stage: guide users to standardize their use, regularly maintain components, and extend the service life of materials and modules; Collect rainwater for greening, irrigation and cleaning, and realize water resources circulation.
Abandonment stage: components are recycled according to the preset dismantling scheme, renewable materials are re-processed, non-renewable materials are treated harmlessly, and the amount of construction waste landfill is reduced.
References
GB/T 7714:Kamali M, Hewage K, Sadiq R. Economic sustainability benchmarking of modular homes: A life cycle thinking approach[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 348: 131290.
MLA:Kamali, Mohammad, Kasun Hewage, and Rehan Sadiq. "Economic sustainability benchmarking of modular homes: A life cycle thinking approach." Journal of Cleaner Production 348 (2022): 131290.
APA:Kamali, M., Hewage, K., & Sadiq, R. (2022). Economic sustainability benchmarking of modular homes: A life cycle thinking approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 348, 131290.